Description
What Is Changa?
Changa is commonly described in research literature as a modern ayahuasca-inspired blend, developed to study the interaction between botanical MAO-inhibiting plants and tryptamine alkaloids. It emerged from contemporary ethnobotanical experimentation and is often referenced in discussions about psychoactive plant synergy.
This formulation is widely examined in anthropology, ethnopharmacology, and botanical chemistry research.
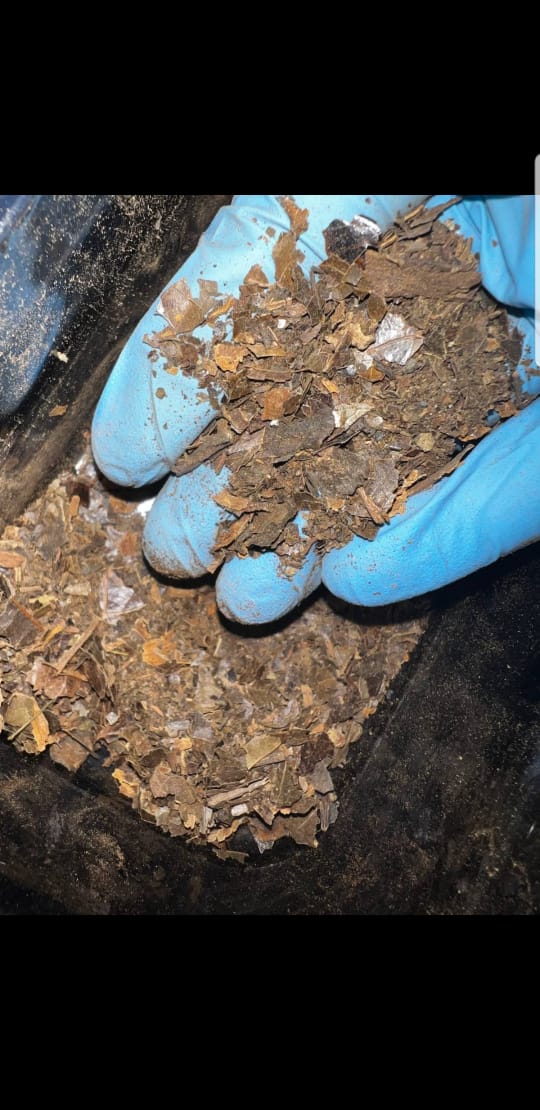
Blend Composition (Reference Formula)
-
33% DMT (reference alkaloid component)
-
33% MAOI botanical sources
-
33% Herbal base, including:
-
Banisteriopsis caapi vine
-
Blue Lotus (Nymphaea caerulea)
-
Damiana (Turnera diffusa)
-
These plants are historically significant and frequently cited in traditional medicine, ceremonial studies, and herbal research.
Research & Academic Interest
Changa is studied for:
-
Ethnobotanical formulation research
-
Alkaloid–plant interaction analysis
-
Ayahuasca analog studies
-
Cultural and historical psychedelic research
-
Aromatic and botanical compound profiling
The inclusion of Caapi vine, a natural source of beta-carbolines, makes this blend particularly relevant for MAOI research discussions.
Botanical Significance
-
Caapi Vine: Central to traditional Amazonian ayahuasca preparations
-
Blue Lotus: Historically used in ancient ceremonial contexts
-
Damiana: Known for aromatic and traditional herbal applications





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.